Vahesumma: €65,00
Inverterkeevitus 355A TIG-LIFT / MMA / MMA-PULSE
€100,00
Technical data
Welding method: TIG-LIFT / MMA / MMA-PULSE
Power supply: 230V/50Hz
Power consumption: 8.6 kVA [TIG]; 11.8 kVA [MMA]
Welding current range for MMA: 20 – 355 A
Welding current range for TIG: 15 – 355 A
Welding current, 100% duty cycle: 255 A
Welding current, duty cycle 60%: 355 A
Rated duty cycle: 60%
Electrode wire diameter: 1.6 – 4 mm
Insulation class: F
Degree of protection: IP21S
Power cable length: 170 cm
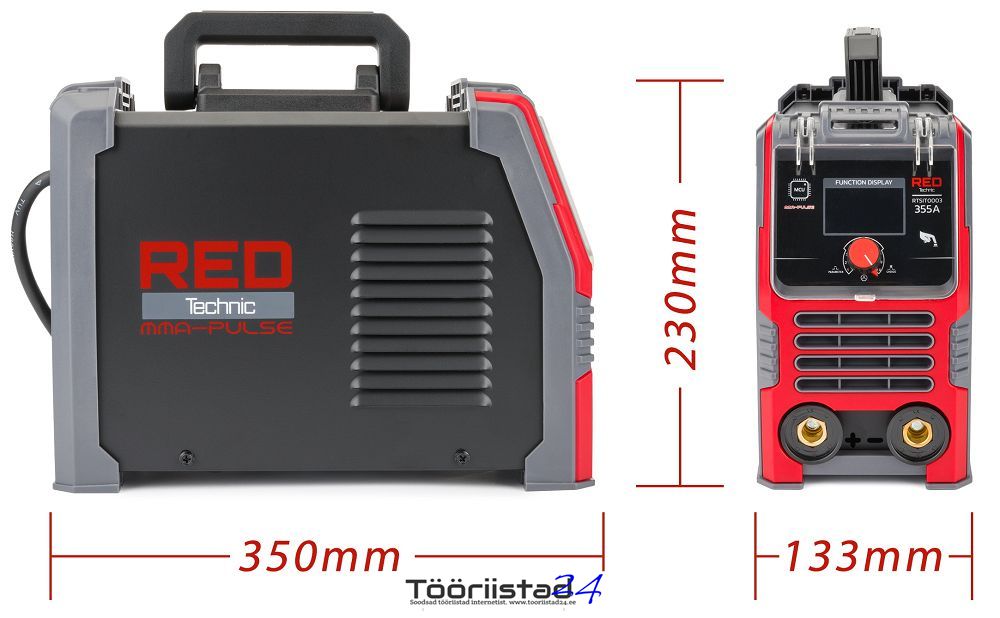
Net device weight: 4.1 kg
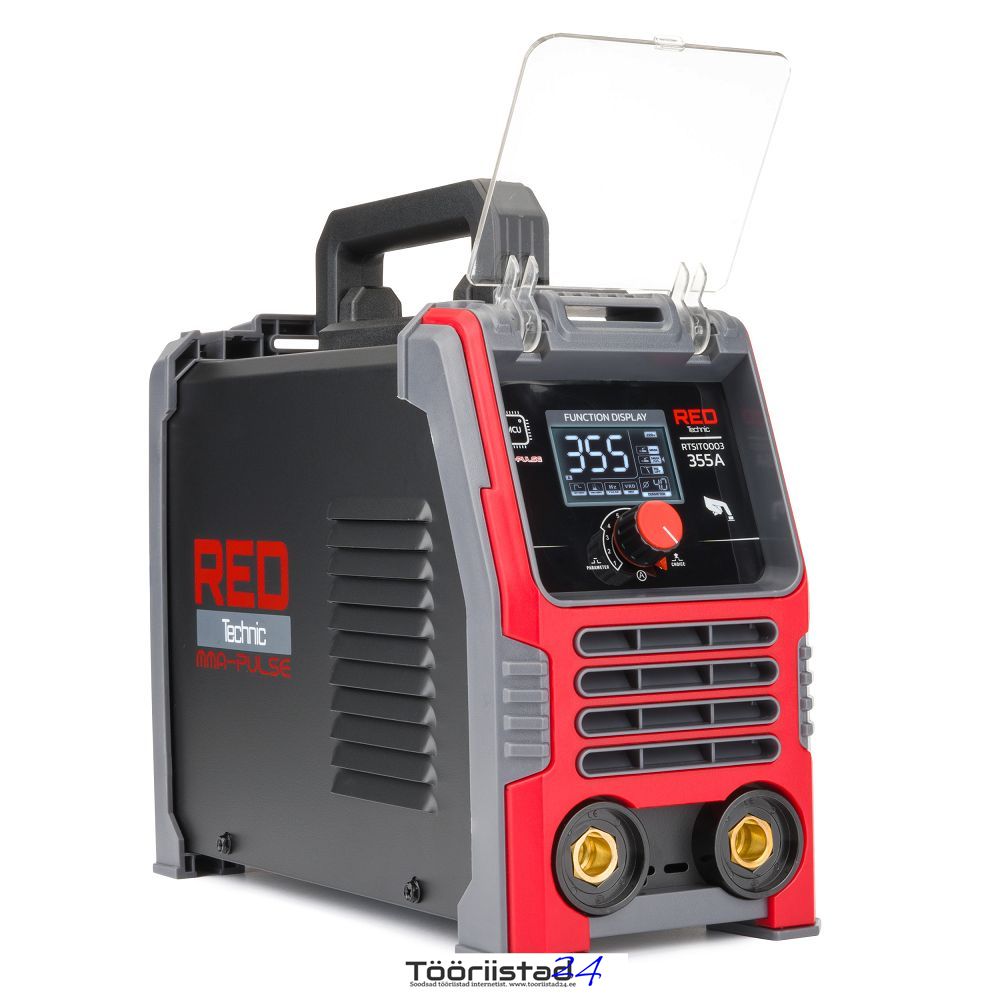
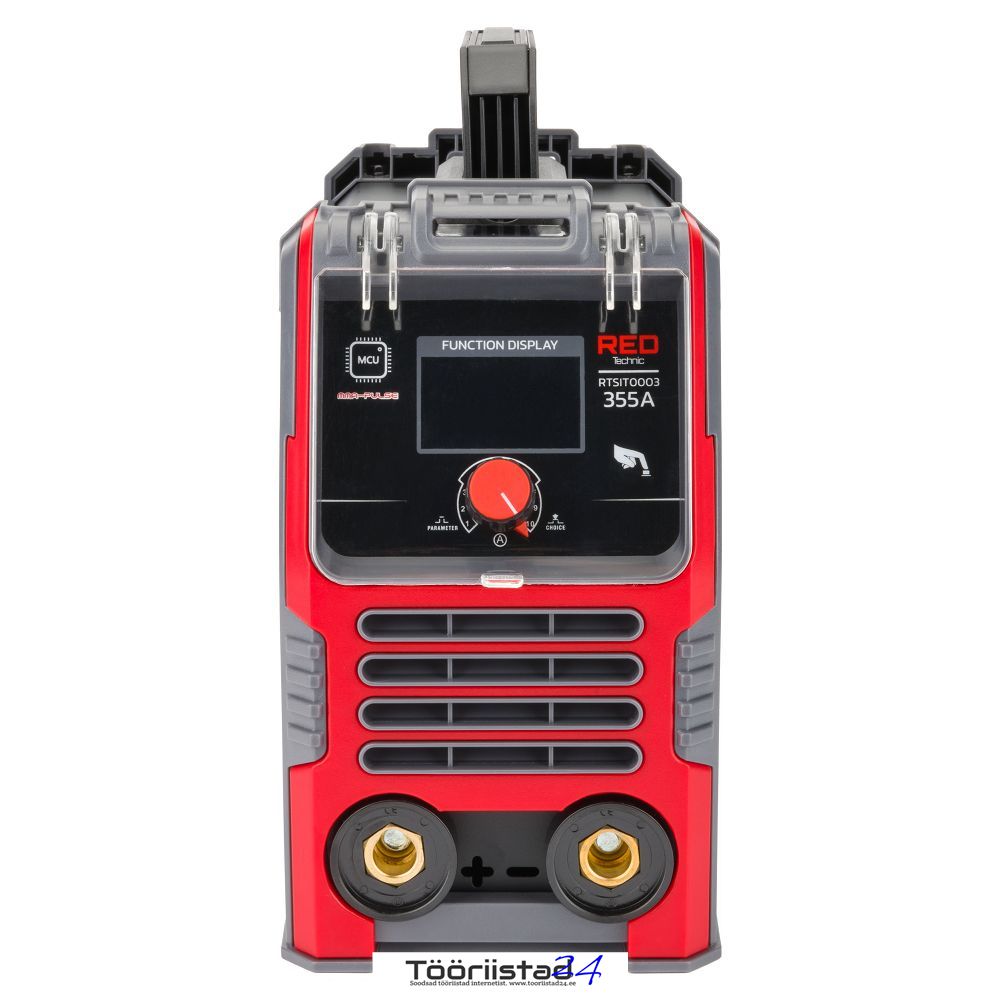
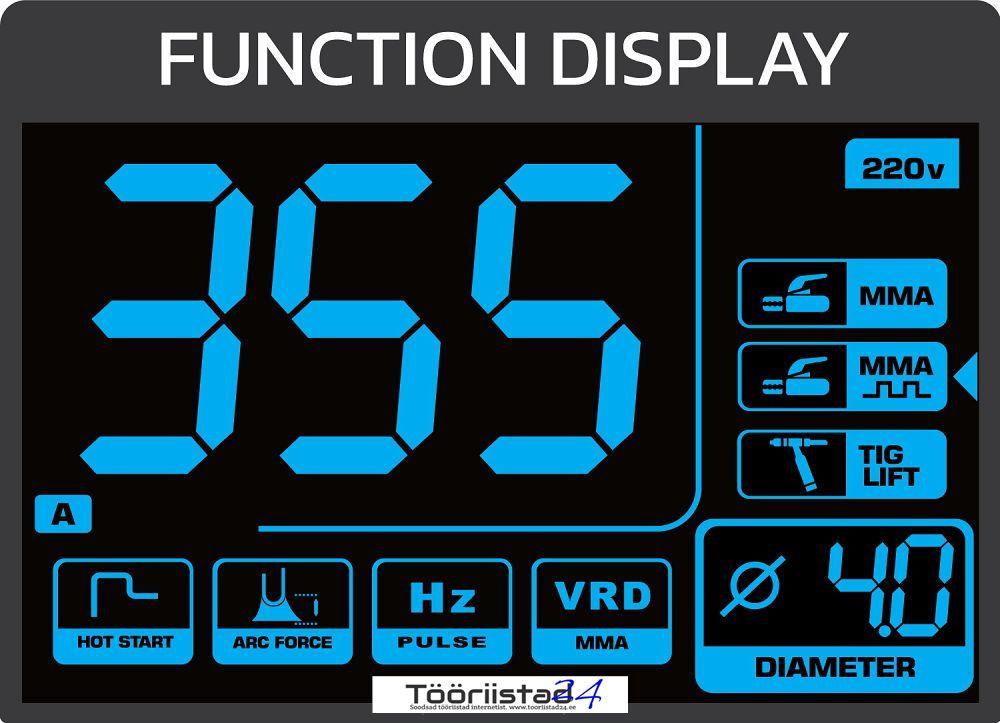
The RTSIT0003 model is an inverter welder whose design is based on efficient IGBT transistors. It is equipped with a clear LCD display indicating the current welding current set by buttons.
The welder is equipped with a fan to cool the electronics and other components, as well as a thermal sensor to protect the device from overheating.
Contents of the set
Welder
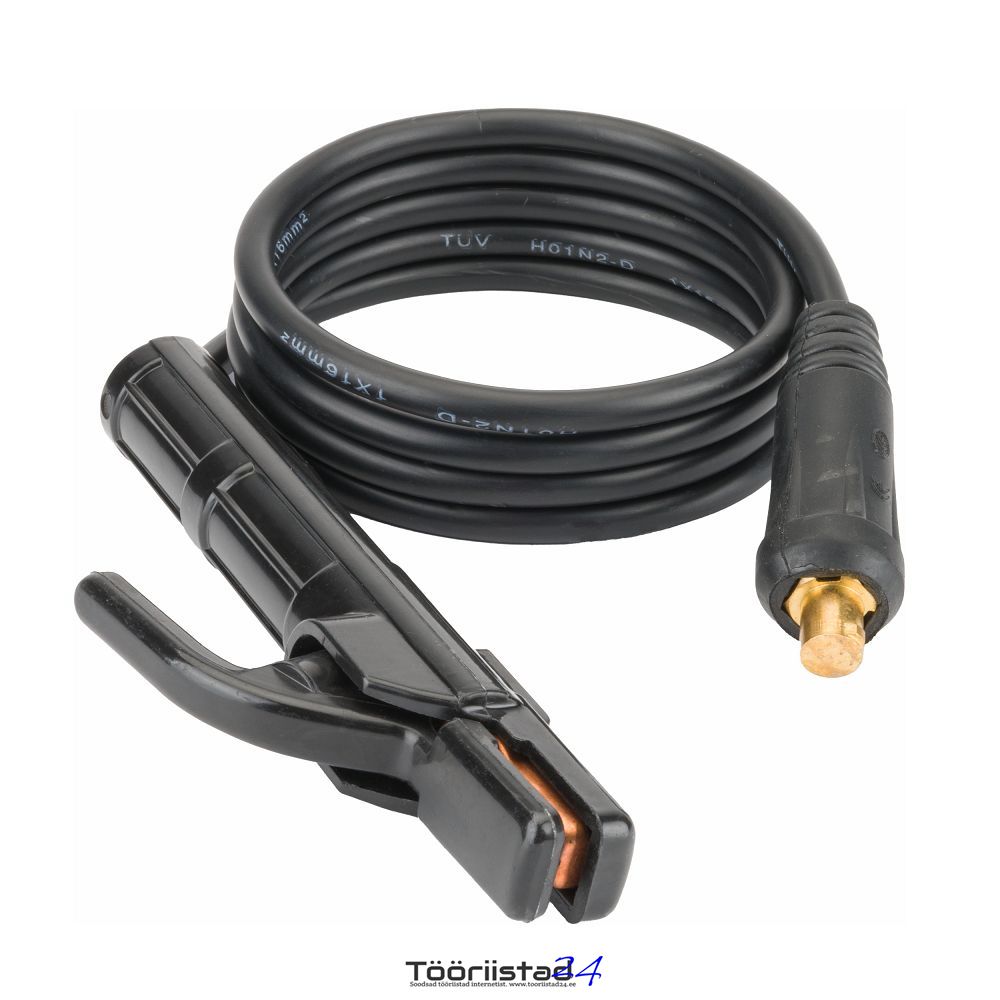
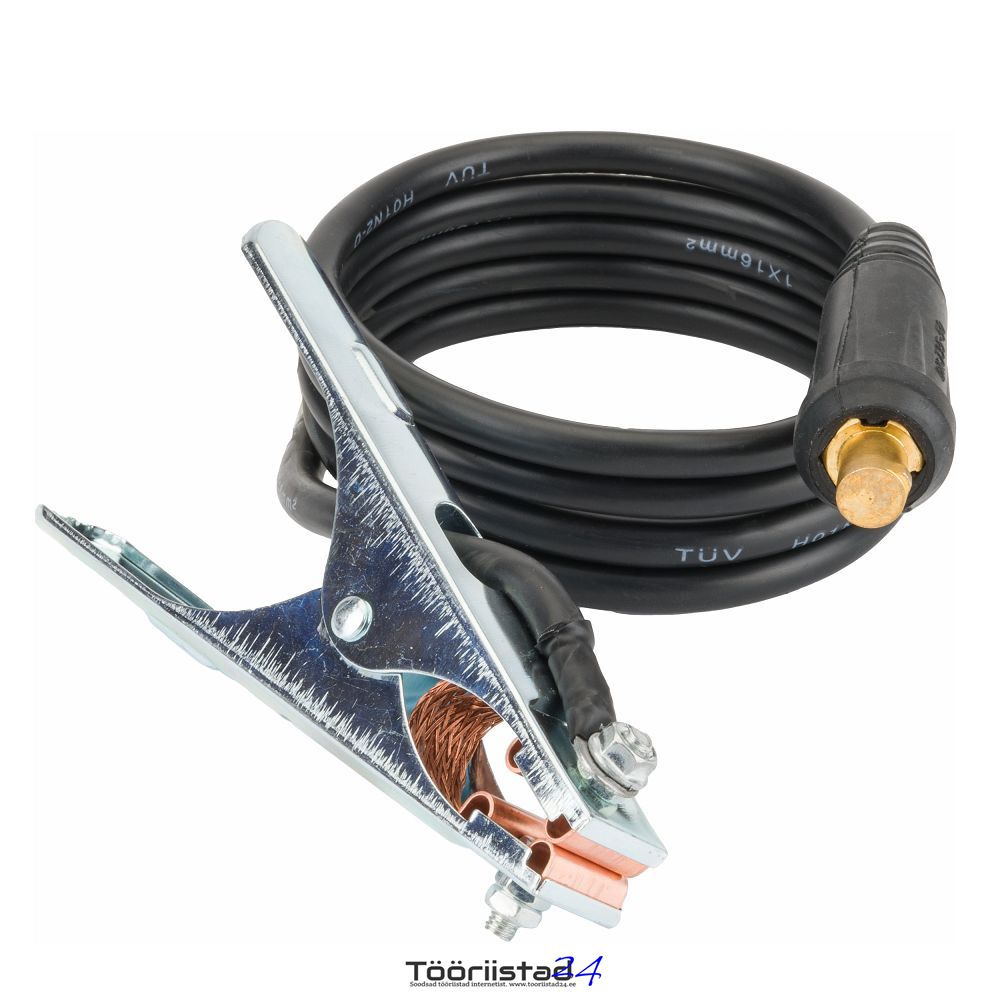
Ground cable (207 cm)
Welding cable (210 cm) / plug diameter 13 mm 35-50
Welding mask
Hammer with brush
Suspension strap
Original packaging
User manual in Polish and English
Additionally:
Professional welding helmet ( PM-APS-600TC )
Magnetic angle up to 11.5 kg ( PM-SKM-11.5 )
Lambskin Welding Gloves
10 pieces of rutile electrodes
RTSIT0003 Device Properties
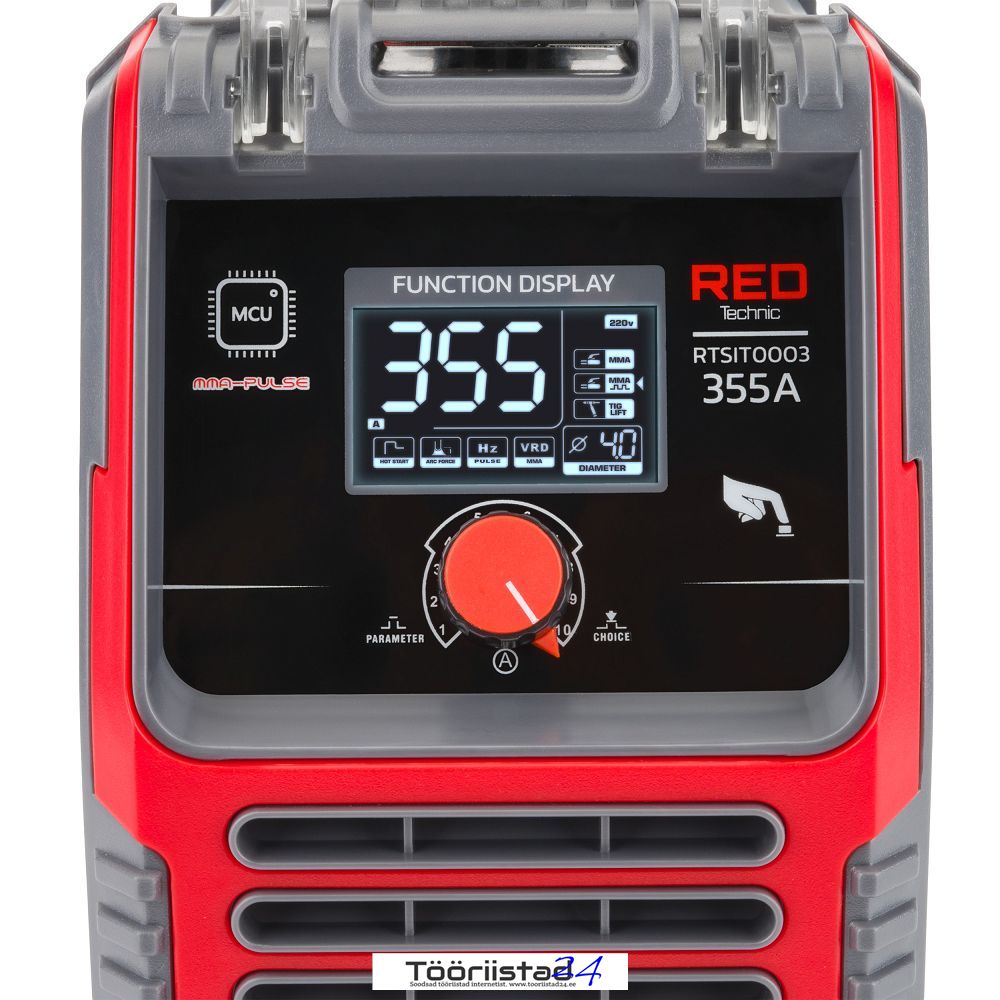
Built-in 3 manually adjustable functions to facilitate work:
HOT START (0-10) popularly called hot start enables a momentary increase in welding current above the value set by the welder. HOT START operates at the moment of arc ignition and is intended to prevent the electrode from sticking to the material. It is a great convenience when igniting the electrode.
ANTI STICK cuts off/minimizes the welding voltage and current in the event of a short circuit between the electrode and the workpiece. ANTI STICK allows the welder to remove the electrode more easily.
ARC FORCE (0-10) stabilizes the arc regardless of its length. Reducing the function values gives a soft arc and a smaller penetration depth, while increasing the function values causes deeper penetration and the possibility of short arc welding. At the highest value for the ARC FORCE function it is possible to “push the electrode into the pool of molten metal and burn the material through. This model has automatic ARC FORCE regulation.
VRD (ON/OFF) is a voltage reduction system that is designed to turn off the power supply within a few milliseconds after welding is finished. This function is also responsible for reducing the voltage on the coated electrode to a safe level. The VRD function turns the welding power supply on and off when the electrical resistance between the electrode and the welded element measured during operation reaches a suitable level. When the device is not working, VRD automatically reduces the voltage of the secondary circuit between the welding tips from 105 V to 14-24 V (this takes a few milliseconds).
DIAMETER – indicator of the recommended electrode diameter when adjusting the welding current.
Compact and minimalist design
The device welds with a current from 20 to 355A, allows welding with an electrode with a diameter of 1.6 mm to 4 mm. The IGBT transistor combines the advantages of two types of transistors: the ease of control of field effect transistors and the high breakdown voltage and switching speed of bipolar transistors. Welding with a 1.6 mm electrode is already possible when using a class C 16A slow-blow fuse. Operation at a maximum current of 355A requires a fuse of at least 20A. The weight of the welder is only 4.1 kg , making it very handy and convenient to transport. The welder has standard, copper EURO welding cable connections. Thanks to the use of the EURO standard, you can easily select additional replacement welding cables. Thanks to the use of a large fan in a small housing of the welder, the air flow has been increased, which lowers the temperature of the transistors. The efficiency of the device is as much as 60%.
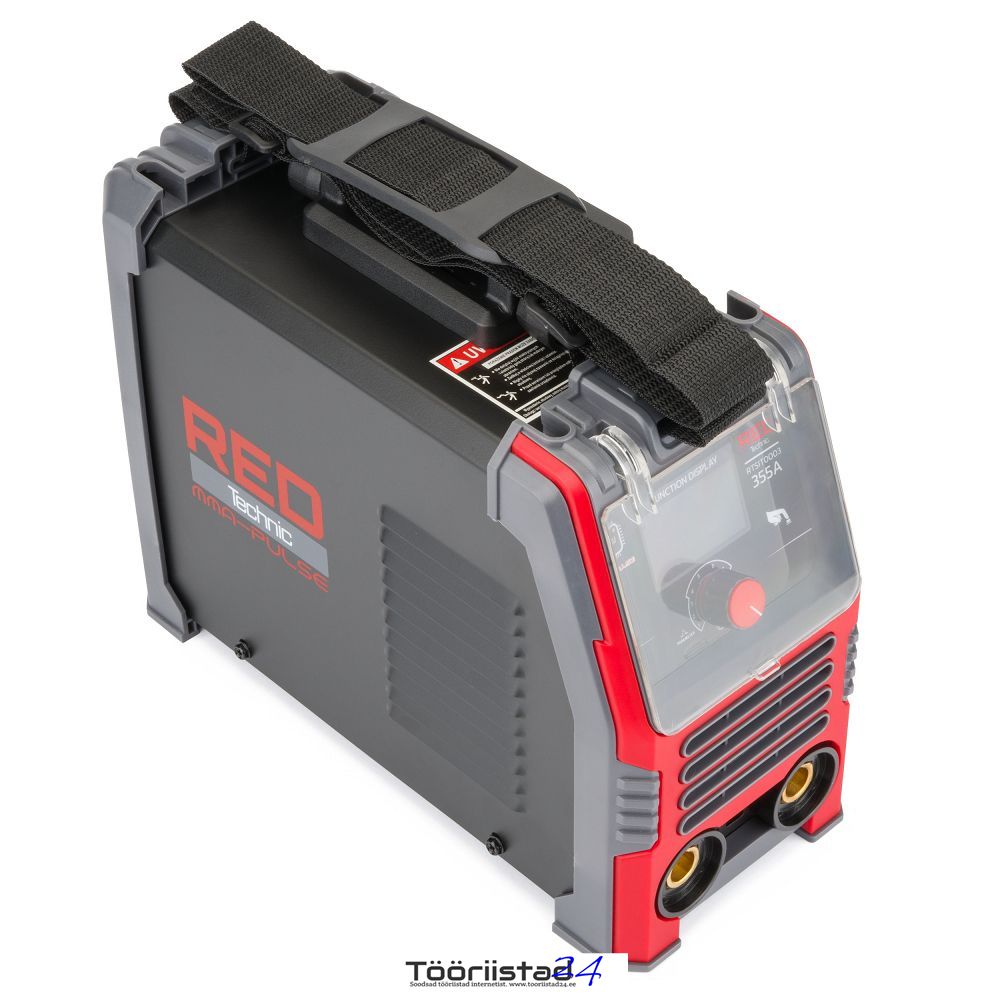
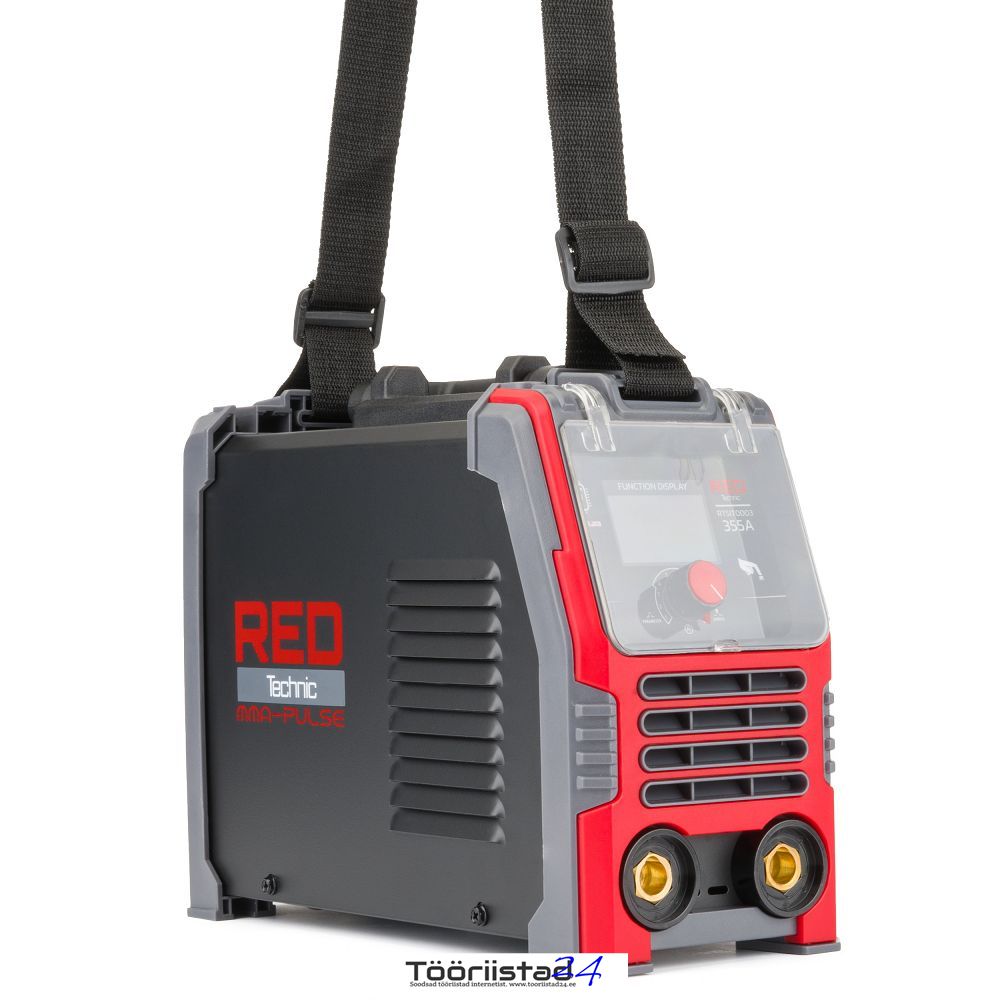
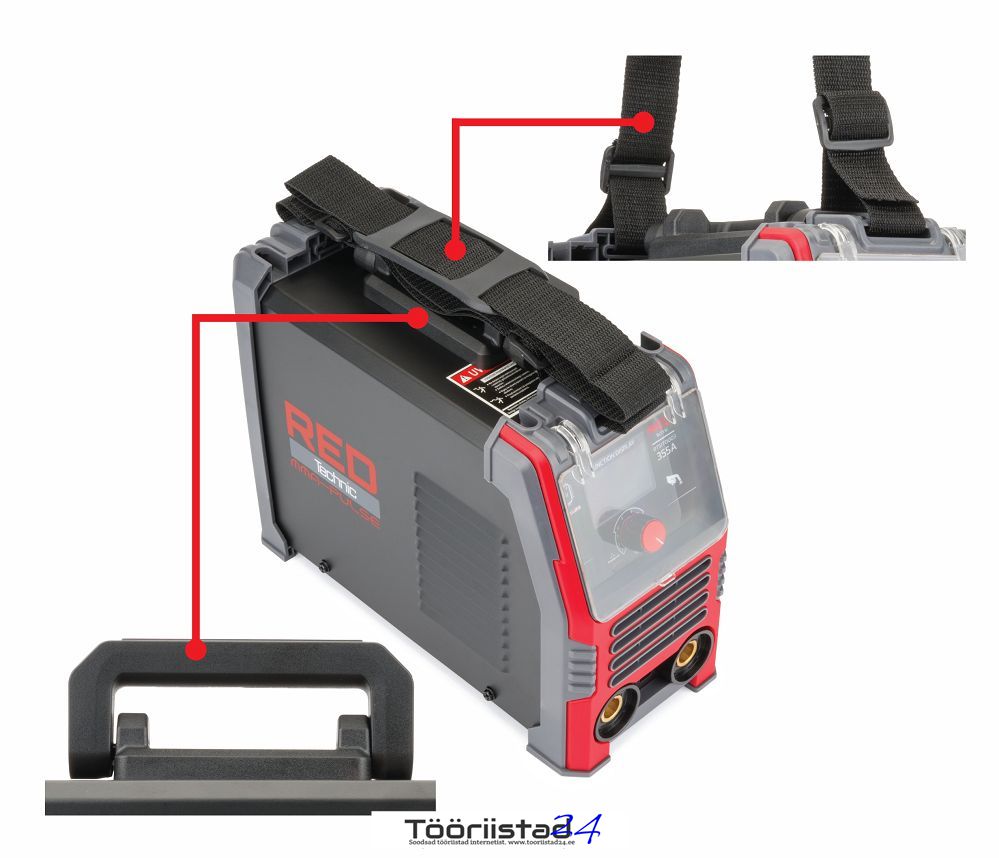
Different methods of transportation
The solid plastic handle allows for easy and very handy movement of the welder thanks to the good balance of the center of gravity. Additionally, the set includes a strap for hanging the device, e.g. on the shoulder, which significantly improves mobile welding, e.g. at heights.
Intuitive and extremely simple operation
The welder is equipped with one button, which also serves as a knob. All parameters on the display are well marked. Function selection is done by short presses, which are precisely marked with arrows highlighting the adjustment of a given parameter. Parameter units such as welding current, percentage of value, or frequency also appear on the display for faster and more intuitive control of welding functions. To change the welding method, simply hold the adjustment button for 10 seconds and then switch the desired welding method with the knob. By adjusting the welding current, the electrode diameter parameter adjusts automatically, suggesting the optimal electrode thickness for the welding current value.
MMA welding
Arc welding with a coated electrode is also called the MMA (Manual Arc Welding) method and is the oldest and most universal method of arc welding. The MMA method uses a coated electrode, which consists of a metal core covered with a compressed coating. An electric arc is generated between the end of the electrode and the welded material. The arc is ignited by contact by touching the end of the electrode to the welded material. The electrode melts and drops of molten metal from the electrode are transferred through the arc to the liquid pool of welded metal, creating a weld after cooling. The welder moves the electrode as it melts to the welded object so as to maintain a constant arc length and at the same time moves its melting end along the weld line. The melting electrode coating emits gases that protect the liquid metal from the effects of the atmosphere and then solidifies and creates slag on the surface of the pool, which protects the solidifying weld metal from the effects of the environment. After moving the electrode away from the welded object, the electric arc stops and the welding process is interrupted. After laying one bead, the slag must be mechanically removed. The basic difference from other welding methods is that in the MMA method the electrode is shortened. In the TIG method, the electrode length remains unchanged at all times and the distance between the holder and the welded element is constant at all times. In the MMA method, in order to maintain a constant distance between the electrode and the weld pool, the electrode holder must be constantly moved towards the welded element, which means that the welder’s skills play a special role.
MMA PULSE welding
This is a modern feature of inverter welders, which additionally has the task of making a high-quality weld, especially when welding stainless steel. Thanks to this method, discoloration is limited and the material does not overheat at the welding point.
TIG welding
TIG welding is a method that allows for obtaining the highest quality welds. The welding arc glows between a high-temperature resistant, non-consumable tungsten electrode and the welded element. The inert gas, from which the method takes its name, creates an oxygen-free atmosphere and prevents chemical reactions in the liquid weld pool. As a result, smooth, even and pore-free welds are created. The filler metal is supplied manually or from a wire feeder. TIG welding is possible for all weldable metals. The largest scope of application is stainless steels and non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum, copper and brass. TIG is primarily used for making the root layer of the weld, because the welds are clean and pore-free, and therefore they withstand dynamic loads well.
✔️Taganemisõigus 14 päeva
✔️Garantii
Laost otsas
Sama toode võib olla laos teise tarnija koodiga. Palun kasuta otsingut või jäta oma e-posti aadress, et saaksime anda teada kui toode on jälle saadaval
Technical data
Welding method: TIG-LIFT / MMA / MMA-PULSE
Power supply: 230V/50Hz
Power consumption: 8.6 kVA [TIG]; 11.8 kVA [MMA]
Welding current range for MMA: 20 – 355 A
Welding current range for TIG: 15 – 355 A
Welding current, 100% duty cycle: 255 A
Welding current, duty cycle 60%: 355 A
Rated duty cycle: 60%
Electrode wire diameter: 1.6 – 4 mm
Insulation class: F
Degree of protection: IP21S
Power cable length: 170 cm
Net device weight: 4.1 kg
The RTSIT0003 model is an inverter welder whose design is based on efficient IGBT transistors. It is equipped with a clear LCD display indicating the current welding current set by buttons.
The welder is equipped with a fan to cool the electronics and other components, as well as a thermal sensor to protect the device from overheating.
Contents of the set
Welder
Ground cable (207 cm)
Welding cable (210 cm) / plug diameter 13 mm 35-50
Welding mask
Hammer with brush
Suspension strap
Original packaging
User manual in Polish and English
Additionally:
Professional welding helmet ( PM-APS-600TC )
Magnetic angle up to 11.5 kg ( PM-SKM-11.5 )
Lambskin Welding Gloves
10 pieces of rutile electrodes
RTSIT0003 Device Properties
Built-in 3 manually adjustable functions to facilitate work:
HOT START (0-10) popularly called hot start enables a momentary increase in welding current above the value set by the welder. HOT START operates at the moment of arc ignition and is intended to prevent the electrode from sticking to the material. It is a great convenience when igniting the electrode.
ANTI STICK cuts off/minimizes the welding voltage and current in the event of a short circuit between the electrode and the workpiece. ANTI STICK allows the welder to remove the electrode more easily.
ARC FORCE (0-10) stabilizes the arc regardless of its length. Reducing the function values gives a soft arc and a smaller penetration depth, while increasing the function values causes deeper penetration and the possibility of short arc welding. At the highest value for the ARC FORCE function it is possible to “push the electrode into the pool of molten metal and burn the material through. This model has automatic ARC FORCE regulation.
VRD (ON/OFF) is a voltage reduction system that is designed to turn off the power supply within a few milliseconds after welding is finished. This function is also responsible for reducing the voltage on the coated electrode to a safe level. The VRD function turns the welding power supply on and off when the electrical resistance between the electrode and the welded element measured during operation reaches a suitable level. When the device is not working, VRD automatically reduces the voltage of the secondary circuit between the welding tips from 105 V to 14-24 V (this takes a few milliseconds).
DIAMETER – indicator of the recommended electrode diameter when adjusting the welding current.
Compact and minimalist design
The device welds with a current from 20 to 355A, allows welding with an electrode with a diameter of 1.6 mm to 4 mm. The IGBT transistor combines the advantages of two types of transistors: the ease of control of field effect transistors and the high breakdown voltage and switching speed of bipolar transistors. Welding with a 1.6 mm electrode is already possible when using a class C 16A slow-blow fuse. Operation at a maximum current of 355A requires a fuse of at least 20A. The weight of the welder is only 4.1 kg , making it very handy and convenient to transport. The welder has standard, copper EURO welding cable connections. Thanks to the use of the EURO standard, you can easily select additional replacement welding cables. Thanks to the use of a large fan in a small housing of the welder, the air flow has been increased, which lowers the temperature of the transistors. The efficiency of the device is as much as 60%.
Different methods of transportation
The solid plastic handle allows for easy and very handy movement of the welder thanks to the good balance of the center of gravity. Additionally, the set includes a strap for hanging the device, e.g. on the shoulder, which significantly improves mobile welding, e.g. at heights.
Intuitive and extremely simple operation
The welder is equipped with one button, which also serves as a knob. All parameters on the display are well marked. Function selection is done by short presses, which are precisely marked with arrows highlighting the adjustment of a given parameter. Parameter units such as welding current, percentage of value, or frequency also appear on the display for faster and more intuitive control of welding functions. To change the welding method, simply hold the adjustment button for 10 seconds and then switch the desired welding method with the knob. By adjusting the welding current, the electrode diameter parameter adjusts automatically, suggesting the optimal electrode thickness for the welding current value.
MMA welding
Arc welding with a coated electrode is also called the MMA (Manual Arc Welding) method and is the oldest and most universal method of arc welding. The MMA method uses a coated electrode, which consists of a metal core covered with a compressed coating. An electric arc is generated between the end of the electrode and the welded material. The arc is ignited by contact by touching the end of the electrode to the welded material. The electrode melts and drops of molten metal from the electrode are transferred through the arc to the liquid pool of welded metal, creating a weld after cooling. The welder moves the electrode as it melts to the welded object so as to maintain a constant arc length and at the same time moves its melting end along the weld line. The melting electrode coating emits gases that protect the liquid metal from the effects of the atmosphere and then solidifies and creates slag on the surface of the pool, which protects the solidifying weld metal from the effects of the environment. After moving the electrode away from the welded object, the electric arc stops and the welding process is interrupted. After laying one bead, the slag must be mechanically removed. The basic difference from other welding methods is that in the MMA method the electrode is shortened. In the TIG method, the electrode length remains unchanged at all times and the distance between the holder and the welded element is constant at all times. In the MMA method, in order to maintain a constant distance between the electrode and the weld pool, the electrode holder must be constantly moved towards the welded element, which means that the welder’s skills play a special role.
MMA PULSE welding
This is a modern feature of inverter welders, which additionally has the task of making a high-quality weld, especially when welding stainless steel. Thanks to this method, discoloration is limited and the material does not overheat at the welding point.
TIG welding
TIG welding is a method that allows for obtaining the highest quality welds. The welding arc glows between a high-temperature resistant, non-consumable tungsten electrode and the welded element. The inert gas, from which the method takes its name, creates an oxygen-free atmosphere and prevents chemical reactions in the liquid weld pool. As a result, smooth, even and pore-free welds are created. The filler metal is supplied manually or from a wire feeder. TIG welding is possible for all weldable metals. The largest scope of application is stainless steels and non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum, copper and brass. TIG is primarily used for making the root layer of the weld, because the welds are clean and pore-free, and therefore they withstand dynamic loads well.
 Jaotusmehhanismi fikseerimiskomplekt AUDI 3.0 A4,A6,A8(2847)
Jaotusmehhanismi fikseerimiskomplekt AUDI 3.0 A4,A6,A8(2847)